< Back
The 10 Best Academic Search Engines You Can't Miss!
Declan Gessel
Sep 19, 2024
Conducting research for an academic paper can be overwhelming. You might be tasked with writing about a topic you know little about or writing a paper about a subject you don’t particularly enjoy. To find sources for essay can be time-consuming and laborious, especially if you lack the tools to streamline the process.
Academic search engines can help you locate scholarly articles, journals, and publications that can help you develop a better understanding of your topic. This guide will introduce you to the ten best academic search engines you can’t miss.
One tool that can help you quickly find sources for your following academic paper is Jotbot’s source finder. This simple AI tool scans the web to find reliable sources for your specific essay or research paper and even helps you create an outline.
Table Of Contents
The Need for Academic Search Engines

Academic research relies heavily on credible, peer-reviewed sources to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented. Scholarly search engines provide direct access to these high-quality sources, essential for writing essays, theses, dissertations, and research papers.
Key Benefits
Peer-reviewed Content
Academic search engines prioritize peer-reviewed articles and publications, ensuring that experts in the field vet the information.
Minimizes Misinformation
Different from general search engines, academic search engines reduce the likelihood of encountering unreliable or non-scholarly content.
Practical Example
A student working on a research paper about climate change can use scholarly search engines like Google Scholar or JSTOR to find peer-reviewed articles from reputable journals, ensuring the validity of their references.
Practical Tip
When conducting academic research, always prioritize academic search engines over general ones to maintain the credibility and quality of your work.
Improved Research Quality
The quality of research is directly linked to the quality of the sources used. Academic search engines provide access to comprehensive databases of scholarly articles, enabling researchers to build a solid foundation for their literature reviews, arguments, and analyses.
Key Benefits
Access to comprehensive databases: Academic search engines like PubMed, ScienceDirect, and IEEE Xplore offer extensive collections of scholarly articles, journals, books, and conference papers across various fields.
In-depth Coverage Of Subjects: These platforms cover a wide range of subjects, providing researchers with diverse perspectives and in-depth analyses, which are crucial for comprehensive literature reviews.
Practical Example: A researcher preparing a literature review on the psychological effects of social media can use PubMed and PsycINFO to access extensive research studies and meta-analyses on the topic.
Practical Tip: Combine different academic search engines to cover all aspects of a research topic, ensuring a well-rounded and comprehensive understanding.
Save Time with Academic Search Engines
Finding credible academic sources on general search engines can take time due to the vast amount of irrelevant or non-academic content. Academic search engines streamline the research process by filtering results to include only scholarly articles, saving time and effort.
Key benefits
Focused search results: Academic search engines are designed to return results relevant to academic and research inquiries, reducing the time spent sifting through unrelated content.
Advanced search filters: Features like advanced search options, Boolean operators, and filters (e.g., by date, author, and publication type) allow users to narrow down results to the most relevant sources quickly.
Practical example: A graduate student researching renewable energy technologies can use ScienceDirect or IEEE Xplore to quickly find the latest peer-reviewed articles, saving time compared to searching on a general platform. Practical tip: Utilize the advanced search filters and Boolean operators available on academic search engines to quickly refine your search results and focus on the most pertinent studies.
Access Specialized Content with Academic Search Engines
Some academic fields require access to very specialized content that may not be readily available through general search engines or even some broad academic search platforms. Specific academic search engines are designed to cater to these specialized needs.
Key benefits
Field-specific search engines: Platforms like PubMed for life sciences and biomedical research, ERIC for education research, and IEEE Xplore for engineering and technology provide access to specialized databases that general search engines cannot match.
Access to niche journals and publications: Some academic search engines provide access to niche journals and magazines essential for research in specific disciplines.
Practical example: An engineering student looking for the latest research on machine learning algorithms in robotics would find IEEE Xplore more beneficial than general academic platforms due to its specific focus on engineering and technology.
Practical tip: Identify which academic search engines specialize in your field and prioritize using them to access the most relevant and cutting-edge research.
Enhanced Citation and Reference Management
Proper citation and referencing are critical aspects of academic writing. Academic search engines often integrate seamlessly with citation management tools, making organizing and formatting references accurately easier.
Key Benefits
Easy integration with citation tools: Many academic search engines allow direct export of citations to tools like Zotero, EndNote, or Mendeley, simplifying the reference management process.
Citation analysis and metrics: Some platforms provide citation analysis tools, helping researchers understand the impact and relevance of a particular article or study.
Practical example: A PhD student writing a dissertation on neuroscience can use PubMed to export citations directly to their preferred citation management tool, ensuring accurate and consistent referencing.
Practical tip: Use the citation management features available on academic search engines to streamline your workflow and maintain proper referencing throughout your research.
Related Reading
• How To Find Good Sources
• Using AI For Research
• Citing ChatGPT
• How To Find Academic Sources
• How To Cite AI In MLA
• AI For Research Paper Writing
• Essay Sources
• AI In Academic Writing
• Most Reliable Sources For Research
• How To Get ChatGPT To Cite Sources
Criteria for Choosing the Best Academic Search Engines

Access to Peer-Reviewed Journals: The Gold Standard for Academic Research
Peer-reviewed journals are the gold standard in academic research, as they undergo rigorous evaluation by experts before publication. An effective academic search engine should prioritize access to these high-quality, vetted sources.
Key Features
Broad Range of Disciplines: Provides access to peer-reviewed journals across multiple disciplines, ensuring comprehensive coverage for interdisciplinary research.
Credible and Reputable Journals: Offers content from well-known publishers and academic institutions, enhancing the reliability of the sources.
Practical Tip: Look for search engines that explicitly mention their focus on peer-reviewed content to ensure the credibility of your research.
User-Friendly Interface and Advanced Search Options: Features to Look For
A user-friendly interface with advanced search options helps researchers quickly find the most relevant sources without getting overwhelmed by irrelevant results. Efficient navigation and search functionality are crucial for saving time and improving research accuracy.
Key Features
Intuitive Navigation: An easy-to-navigate layout with a clean and organized design that makes finding and filtering research papers, articles, and journals simple.
Advanced Search Filters: Options to refine searches by author, date, publication type, keywords, language, and more to help users zero in on the most pertinent sources.
Boolean Operators and Search Commands: Supports advanced search queries using Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) and specific search commands to enhance precision.
Practical Tip: Choose search engines with robust filtering options and an intuitive design to streamline the research process and minimize frustration.
Free vs. Subscription Access: What’s the Difference?
Access to academic content can vary from fully open-access platforms to those requiring a subscription or institutional access. Understanding the cost structure is essential for choosing a search engine that aligns with your budget and access capabilities.
Key Features
Open Access Options: This site offers a significant amount of free, open-access content, allowing users to access full-text articles without subscription fees.
Hybrid Access Models: Combines free access with subscription-based content, providing a broader range of options for researchers with different needs.
Clear Subscription Information: Provides transparent information about access levels, costs, and subscription plans.
Practical Tip: Prioritize academic search engines that offer a mix of free and subscription content to maximize access to high-quality sources while effectively managing costs.
Integration with Citation Management Tools: Why It Matters
Properly managing and formatting citations is a critical aspect of academic writing. Academic search engines that integrate seamlessly with citation management tools like Zotero, EndNote, and Mendeley simplify organizing and citing sources.
Key Features
Direct Export to Citation Tools: Offers easy export options for citations directly to popular management tools, ensuring quick and accurate reference handling.
Multiple Citation Formats: It supports various citation styles (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) for different academic disciplines, making it easier to adhere to specific guidelines.
Automatic Citation Generation: It provides tools to generate citations automatically, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
Practical Tip: Choose search engines that provide robust integration with citation management tools to save time and ensure accurate referencing in your academic work.
Availability of Full-Text Articles: Why It Matters
Access to full-text articles is essential for conducting thorough research. Some academic search engines provide only abstracts or summaries, requiring additional steps to access the full content.
Key Features
Direct Links to Full-Text Articles: Access to full-text article versions makes reviewing and analyzing the complete study easier.
Institutional and Open Access: Provides options for accessing full texts through institutional subscriptions or open-access repositories.
Abstracts and Summaries for Initial Review: This section includes detailed abstracts or summaries to help users determine an article's relevance before accessing the full text.
Practical Tip: Opt for search engines that indicate whether full-text articles are available or if they are behind a paywall to plan your research strategy accordingly.
Multidisciplinary Coverage and Niche Focus: How to Choose
Researchers often require access to sources from various disciplines or need highly specialized content. An excellent academic search engine should provide multidisciplinary coverage or cater specifically to niche fields of study.
Key Features:
Comprehensive Subject Coverage: Supports research across various fields, from humanities and social sciences to science, technology, and medicine.
Specialized Databases for Niche Research: Offers specialized databases for specific fields, such as PubMed for biomedical research or IEEE Xplore for engineering and technology.
Cross-Disciplinary Search Capabilities: Allows for searches that span multiple fields, facilitating interdisciplinary research.
Practical Tip: Use search engines that offer broad and specialized content to access various academic materials tailored to your research needs.
Write more intelligently, not harder, with Jotbot's AI writing assistant. Start finding sources that are accessible with Jotbot's source finder today. Sign in with Google and get started in seconds.
The 10 Best Academic Search Engines You Can't-Miss
1. Google Scholar: Your Go-To for Academic Research
Google Scholar is a free academic search engine that covers a broad range of scholarly literature across disciplines, from articles and theses to conference papers and court opinions. It’s one of the most widely used academic search engines on the web and can help users quickly find relevant material for their research projects.
Unique Features
Google Scholar’s ‘Cited By’ function allows users to see how many times an article has been cited by other works, which can help determine its impact and relevance. The search engine also has alerts for new research, so users can set up alerts for specific keywords to stay updated on the latest research developments in their field.
Google Scholar seamlessly integrates with Google Drive, so users can easily save articles and citations to their Drive for future access and organization.
Limitations
While Google Scholar can be an excellent resource for academic research, it does include some non-peer-reviewed content, such as unpublished papers, which may require additional scrutiny.
Practical Tip
Use the "Advanced Search" feature to filter by author, publication, and date to find the most relevant and credible sources.
2. PubMed: The Life Sciences Search Engine

PubMed is a free search engine maintained by the National Library of Medicine, specializing in life sciences and biomedical research. It provides access to over 30 million citations from the MEDLINE database, journals, and books.
Unique Features
PubMed offers advanced search filters and robust search options to filter results by publication type, subject, age, and more. The search engine also links to full-text articles available on publishers’ websites or within PubMed Central for free access. Additionally, PubMed includes a vast repository of clinical trials and systematic reviews.
Limitations
While PubMed is one of the best resources for biomedical and life sciences fields, users may need institutional access for some full-text articles.
Practical Tip
Utilize PubMed’s "MeSH" (Medical Subject Headings) feature to refine searches and ensure precision in retrieving relevant biomedical literature.
3. JSTOR: A Trusted Academic Source

JSTOR provides access to thousands of academic journals, books, and primary sources across various disciplines, including humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Unique Features
JSTOR is known for its high-quality, peer-reviewed content, making it a trusted source for academic research. The search engine offers reliable, high-quality articles invaluable for humanities and social sciences research.
JSTOR also provides access to historical documents, images, and primary sources. Its text analyzer tool allows users to upload their text or documents to find relevant articles and sources based on the content.
Limitations
Most content is behind a paywall or requires institutional access. JSTOR also has limited access to recent articles.
Practical Tip
Take advantage of JSTOR’s free monthly access to a limited number of articles by signing up for a personal account.
4. IEEE Xplore: Engineering and Technology Research
IEEE Xplore is a digital library that provides access to a vast collection of literature in engineering, computer science, and electronics. It is trendy among researchers in these fields.
Unique Features
IEEE Xplore offers exclusive access to IEEE’s comprehensive collection of technical standards, conference proceedings, and cutting-edge research. The digital library also features sophisticated search options that allow users to filter by subject, publication type, and year. Users can set up alerts to notify them when selected articles are cited in new publications.
Limitations
IEEE Xplore offers most full-text content through a subscription or institutional access. Access to non-engineering fields is also limited.
Practical Tip
Use IEEE Xplore for engineering and technology-related research to access the most authoritative and up-to-date studies in these fields.
5. Scopus: Broad Coverage for Scientific Literature
Scopus is an abstract and citation database that provides comprehensive coverage across scientific, technical, medical, and social sciences disciplines.
Unique Features
Scopus allows users to see the impact of research articles and explore the profiles of authors, including their publication history and h-index. The search engine seamlessly integrates with institutional libraries for easy access to full-text content. Scopus includes advanced tools for analyzing search results by author, institution, or funding body.
Limitations
As a subscription-based resource, access to Scopus may be restrictive for independent researchers without institutional support.
Practical Tip
Use Scopus for comprehensive literature reviews and citation tracking to ensure a thorough understanding of research trends and influential studies.
6. ScienceDirect: A Leading Scientific Database
ScienceDirect is a leading full-text scientific database that offers access to articles, book chapters, and reference works in science, technology, medicine, and the social sciences.
Unique Features
ScienceDirect provides extensive full-text access to Elsevier’s prestigious journals and books. The database features advanced search functionality that allows users to narrow down results by article type, discipline, and publication date. ScienceDirect also directly links cited references within articles to facilitate deeper exploration of topics.
Limitations
Most content within ScienceDirect is subscription-based, with limited access to some free content.
Practical Tip
Consider using ScienceDirect when deep-diving into specific scientific fields that require extensive, high-quality, full-text access.
7. ERIC: Focused on Education Research
ERIC is an online digital library that focuses on education research and provides access to scholarly articles, reports, conference papers, and other education-related resources.
Unique Features
ERIC offers free access to extensive education-related documents, reports, and peer-reviewed articles. The digital library specializes in education research, making it highly relevant for teachers, policymakers, and academics in the education field. ERIC provides straightforward search functionality with various filters to refine results.
Limitations
ERIC is limited to education and related fields, which may need to be more helpful for interdisciplinary research.
Practical Tip
Use ERIC for comprehensive research in education and related fields, especially when looking for policy papers and educational research reports.
8. BASE: Access Open-Access Research

BASE aggregates open-access academic resources from over 8,000 content providers, making it one of the world’s most comprehensive search engines for educational resources.
Unique Features
BASE supports searches in multiple languages, making it accessible to a broader audience. The search engine provides access to over 240 million documents from institutional repositories and other open-access repositories. BASE also allows users to filter by document type, language, year, and more.
Limitations
Not all content in BASE is peer-reviewed, so users need to verify the credibility of sources.
Practical Tip
Use BASE to find open-access content across various disciplines and languages, significantly when budget constraints limit access to subscription-based resources.
9. ResearchGate: Connect with Peers

ResearchGate is a social networking platform for scientists and researchers to share papers, ask questions, and collaborate. The platform provides access to millions of research papers, datasets, and discussions.
Unique Features
ResearchGate allows researchers to upload their papers, making them freely available to other users. The platform offers features like project management, Q&A, and direct messaging for networking and collaboration. ResearchGate also provides metrics on reads, citations, and recommendations for shared papers.
Limitations
Access to full-text papers on ResearchGate may depend on author permissions, and not all uploaded content is peer-reviewed.
Practical Tip
Use ResearchGate to network with peers and access research papers directly from authors, mainly when institutional access is unavailable.
10. SSRN: Preprints and Early Research
The Social Science Research Network is a repository for preprints and working papers in the
social sciences and humanities. It offers access to thousands of research papers, working papers, and early-stage research.
Unique Features
SSRN provides free open access to preprints, working papers, and early-stage research. The repository includes filtering options by field, topic, and publication type to narrow down search results. SSRN allows researchers to engage with emerging research before it is published in peer-reviewed journals.
Limitations
Not all papers on SSRN are peer-reviewed, and some content may require additional validation.
Practical Tip
Use SSRN to stay updated on the latest research in the social sciences and humanities.
Related Reading
• Reference Finder
• Best AI For Research
• How to Cite AI
• AI For Literature Review
• Websites Like Google Scholar
• AI That Cites Sources
• Best AI Tool For Research
• Academic Research Software
• How To Use Chat GPT For Research
• Best Research Tools For Students
How to Use Academic Search Engines Effectively

Refine Your Search Terms Like a Pro
The accuracy and relevance of search results depend primarily on the search terms used. Specific keywords and phrases help narrow search results to the most pertinent articles and studies.
How to Do It
Use Specific Keywords and Phrases: Instead of broad terms, use more specific keywords related to your research topic. For example, instead of searching for “climate change,” use “climate change impact on polar bear habitats.”
Utilize Boolean Operators: To refine searches, use Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT). For example, “climate change AND polar bears” or “climate change NOT politics.”
Apply Quotation Marks for Exact Phrases: Search for exact phrases by placing them in quotation marks, e.g., “machine learning algorithms in healthcare.”
Practical Tip
Start with broader terms and gradually refine them by adding specific keywords or Boolean operators to identify the most relevant sources.
Utilize Advanced Filters
Advanced search filters allow users to narrow down results by various criteria, such as publication date, author, document type, and subject area, ensuring more targeted and relevant findings.
How to Do It
Filter by Publication Date: Use date filters to access the most recent research or to focus on studies within a particular time frame.
Select Document Types: Depending on the research need, you can filter results by document types, such as peer-reviewed articles, reviews, theses, books, or conference papers.
Refine by Subject Area: Choose specific subjects or disciplines to avoid irrelevant results from unrelated fields.
Practical Tip
Always use filters to narrow down search results and save time. Most academic search engines, such as Google Scholar and PubMed, provide advanced filtering options that are easy to use.
Check for Full-Text Availability
Access to the full text of articles is crucial for in-depth analysis and understanding. Some search engines provide only abstracts or summaries, requiring additional steps to access the full content.
How to Do It
Look for “Full-Text Available” Links: Many academic search engines indicate whether the full text is available directly or through a partner site. Prioritize sources with full-text access.
Use Institutional Access or Open Access Repositories: If an article is not free, check if your institution has access or is available in an open-access repository.
Request Articles Directly from Authors: Platforms like ResearchGate allow you to request full-text versions directly from the authors if they are not publicly available.
Practical Tip
If the full text is unavailable, check if it can be accessed through tools like the Open Access Button or Unpaywall, which help find free versions of paywalled articles.
Use Alerts and Notifications
Keeping up with the latest research is critical to staying current in any academic field. Setting up alerts and notifications helps researchers stay informed about new publications and developments related to their topics of interest.
How to Do It
Set Up Alerts for Specific Keywords: Most academic search engines, like Google Scholar and Scopus, offer alert features for specific keywords or topics.
Follow Journals or Authors: Subscribe to alerts from specific journals or follow prolific authors to receive notifications about their latest publications.
Use Citation Alerts: Set alerts to notify you when a particular article has been cited in new research, indicating its growing impact and relevance.
Practical Tip
Regularly review and adjust your alerts to focus on the most relevant and impactful research in your field.
Leverage Unique Features of Each Search Engine
Different academic search engines offer unique features that can enhance research effectiveness. Understanding and utilizing these features can help researchers access more relevant, high-quality sources.
How to Do It
Use “Cited By” and “Related Articles” Features: Tools like Google Scholar and PubMed provide “Cited By” and “Related Articles” options to explore articles that cite a particular study or are related by topic.
Text Analyzer Tool on JSTOR: Upload your text to JSTOR’s Text Analyzer to find relevant articles based on your content.
MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) on PubMed: Use the MeSH feature on PubMed to refine searches for biomedical literature more precisely.
Practical Tip
Familiarize yourself with the unique features of the academic search engines you use frequently and incorporate them into your search strategies for more targeted and efficient research.
Combine Multiple Search Engines
Relying on a single search engine may limit access to a comprehensive range of research materials. Combining different search engines can provide a broader perspective and more diverse sources.
How to Do It
Start Broad, Then Narrow Down: Use a general academic search engine like Google Scholar for an initial broad search, then move to specialized ones like PubMed or IEEE Xplore for more focused searches.
Cross-Check Results Across Platforms: Compare results from multiple search engines to identify the most cited and authoritative sources.
Diversify Search Strategies: Use different keywords, phrases, and search filters across platforms to capture a wide range of relevant studies.
Practical Tip
Keep a record of which search engines yield the best results for specific topics or disciplines and develop a multi-platform search strategy accordingly.
Write more intelligently, not harder, with Jotbot's AI writing assistant. Start finding sources for free with Jotbot's source finder today. Sign in with Google and get started in seconds.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Academic Search Engines

Why Limiting Your Search to One Academic Database Can Hurt Your Research
Using only one academic search engine limits access to various available resources. No single search engine covers every academic journal or database, which can restrict the depth and breadth of research.
By sticking to just one search engine, researchers might miss out on essential studies or alternative viewpoints published elsewhere. To avoid this issue, use multiple search engines. To ensure comprehensive coverage, combine general academic search engines like Google Scholar with specialized ones such as PubMed (for life sciences) or IEEE Xplore (for engineering and technology). Next, cross-check results.
Compare findings across different platforms to identify the most authoritative and frequently cited studies. Finally, maintain a list of academic search engines relevant to your field and routinely use at least two or three of them for thorough literature reviews.
Why You Shouldn't Overlook Advanced Search Features When Using Academic Search Engines
Advanced search features, such as Boolean operators, filters, and specific search commands, are essential for narrowing down search results and finding the most relevant articles quickly. Using advanced filters or search operators often results in irrelevant or loosely related content, making it easier to locate valuable sources.
To avoid this issue, learn and use advanced search techniques. Familiarize yourself with Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), wildcards, and exact phrase searches to refine search results. Next, utilize filters. Always apply filters for publication date, document type, author, and subject area to narrow down search results to the most pertinent articles. Finally, take time to learn the advanced search features of each academic search engine and use them consistently to streamline the research process.
Why Credibility Matters When Using Academic Search Engines
Academic search engines sometimes include non-peer-reviewed content, conference abstracts, or unpublished papers that may not be as reliable as peer-reviewed journal articles. Using such sources with proper vetting can ensure the quality of research is maintained. Believing that everything indexed by an academic search engine is peer-reviewed and credible can lead to using unreliable sources in academic writing.
To avoid this issue, verify the source’s peer-review status. Check if the article is published in a reputable, peer-reviewed journal. Most academic search engines provide indicators or filters for peer-reviewed content. Next, evaluate the journal’s reputation. Research the journal’s impact factor, editorial board, and publishing practices to assess its credibility. Finally, always cross-check the peer-review status and credibility of journals and articles before including them in your research.
Why You Should Always Save and Cite Sources Correctly When Using Academic Search Engines
Properly saving and citing sources is crucial for maintaining academic integrity, avoiding plagiarism, and ensuring easy reference during the writing process. Failing to do so can result in lost references, duplicated work, or accidental plagiarism.
Save sources correctly to avoid finding them again or incorrect citations. To avoid this issue, use citation management tools. Tools like Zotero, Mendeley, and EndNote integrate with most academic search engines and help organize and manage citations effectively.
Next, create a reference list as you go. Always compile a list of references as you research to ensure you don’t lose track of essential sources. Finally, regularly back up your citation library and maintain detailed notes on each source to avoid confusion later.
Why You Shouldn't Stop Reading Article Abstracts When Using Academic Search Engines
Accessing only the abstract or summary of an article without reviewing the full text can lead to misinterpretations or incomplete understanding of the research findings. Relying solely on abstracts can result in superficial analysis and a lack of depth in understanding the study’s methodologies, limitations, and conclusions. To avoid this issue, ensure full-text access.
Access the full text of articles whenever possible to get a complete picture. If the full text is unavailable, check if your institution provides access or use tools like Unpaywall to find open-access versions. Next, request full texts from authors. Use platforms like ResearchGate to request full texts directly from authors if they are not publicly available. Make it a habit to read the full text of articles rather than relying on abstracts to ensure comprehensive understanding and robust analysis.
Why Staying Updated with Recent Research Is Crucial for Your Academic Writing
Academic research constantly evolves, and staying updated with the latest studies and developments is crucial for maintaining relevance and accuracy in any field. Relying on old or outdated studies without checking for more recent research can lead to a lack of current context and outdated conclusions. To avoid this issue, set up alerts for new research.
Use alert features on academic search engines to receive notifications about new publications on specific topics. Next, review recent citations. Always check the most recent citations to ensure you reference the latest studies and perspectives. Regularly review alerts and recent studies to ensure your research is current and incorporates the latest findings.
How Jotbot Can Help Streamline Your Research Process
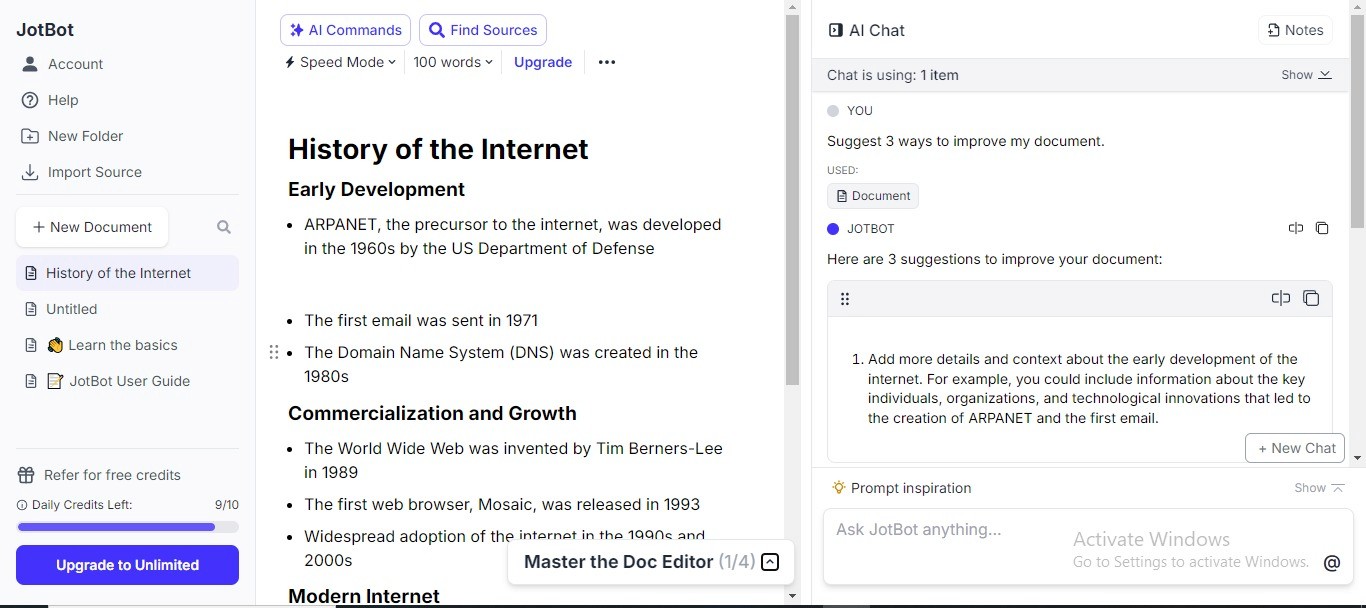
The Smart Way to Find Sources for Your Next Paper
Finding credible and relevant academic sources is a critical part of any research project. However, sifting through vast databases to find suitable sources can be daunting and time-consuming. Jotbot’s AI-powered source finder speeds up the process so you can focus on your research.
Jotbot uses AI algorithms to search across multiple academic databases and search engines, providing a curated list of the most relevant and credible sources. The all-in-one research assistant also automatically filters results to prioritize peer-reviewed journals, highly cited articles, and reputable publishers, ensuring you access only the most authoritative content. Jotbot even offers quick summaries of each source, allowing you to assess the relevance of an article without having to read it in its entirety.
For example, a student researching the impact of social media on mental health can use Jotbot to find the most cited and peer-reviewed articles on the topic, significantly reducing the time spent on manual searches. To get started, use Jotbot’s AI-powered source finder at the start of your research to quickly gather a list of reliable sources, then refine your search with specific keywords and filters.
Get Organized with AI Note-Taking and Summarizing
Organizing and summarizing information from multiple sources can be overwhelming. Effective note-taking and summarizing help distill large volumes of information into manageable insights. Jotbot can summarize lengthy academic articles, extracting the main points, critical arguments, and conclusions to provide a concise overview. Users can take structured notes directly within the platform, linking notes to specific articles or research questions for easy reference.
Jotbot also allows users to highlight important sections and add personal annotations, making it easier to review and synthesize information later. For example, a researcher working on a literature review can use Jotbot to summarize multiple articles and quickly compile a comprehensive overview of the existing research. To get started, leverage Jotbot’s summarization tool to understand an article’s content quickly before diving deeper, saving time and ensuring that only the most relevant sources are read in full.
Let AI Help You Write Your Next Essay
Structuring an essay or research paper is a crucial step that can be challenging for many students and researchers. A well-organized outline helps clarify the argument and ensures logical flow. Jotbot can help you get started. The AI writing assistant automatically generates comprehensive outlines based on research topics, providing a clear structure for the introduction, body, and conclusion sections. Jotbot also offers writing prompts and suggestions to help users expand on each section of the outline, ensuring that all key points are covered.
Users can leverage AI to draft paragraphs or sections of the essay based on the outline and provided notes, streamlining the writing process. For example, a student struggling to structure an argumentative essay on climate policy can use Jotbot to create a detailed outline, receive guidance on expanding each section, and even draft initial paragraphs. First, use the essay outlining feature to plan your writing thoroughly, ensuring all critical points are covered and your argument is presented clearly.
Simplify Citation Management and Formatting
Properly managing citations is essential to maintaining academic integrity and avoiding plagiarism. However, manually formatting citations can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Jotbot simplifies the process with automatic citation generation, which creates citations in various styles (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) based on the selected academic sources, ensuring accuracy and consistency. The all-in-one research assistant seamlessly integrates with popular citation management tools like Zotero, EndNote, and Mendeley for streamlined reference management.
Jotbot automatically formats inline citations and creates bibliographies, saving time and reducing manual effort. For example, a researcher writing a thesis can use Jotbot to manage all references, generate citations in the required style, and create a bibliography with just a few clicks. To get started, regularly update your citation library in Jotbot to keep track of all sources and ensure your references are formatted correctly as you write.
Collaborate Seamlessly with Jotbot
Academic research often involves collaboration with peers, advisors, or co-authors. Jotbot enhances teamwork and productivity with tools that facilitate easy sharing and collaborative editing. The platform allows multiple users to take notes, annotate, and edit documents in real-time, making collaboration smoother and more efficient.
Jotbot also tracks changes made by different collaborators, allowing users to revert to previous versions or see who contributed what. Direct sharing options enable researchers to share their findings and notes and draft documents directly with collaborators or export them in various formats.
For example, a research team working on a joint paper can use Jotbot to collaborate on research notes, draft sections, and manage citations collectively, ensuring consistency and coherence. To get started, use Jotbot’s collaboration features to manage team-based research projects more effectively, ensuring seamless communication and document management.
Write Smarter With Jotbot's Source Finder — Start Writing for Free Today
Finding reliable sources is crucial to writing a solid academic paper. Jotbot's source finder makes the process easy. After you write a prompt to start your essay, Jotbot will find your sources. The first step is to write an essay prompt or a research question to help narrow your search.
Next, Jotbot AI will generate a list of relevant sources for your topic, pulling from academic databases, Google Scholar, and other reputable research websites. You can even use the AI to help summarize the sources and generate citations in your desired format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Write more brilliantly, not harder, with Jotbot's AI writing assistant. Start finding sources for free with Jotbot's source finder today. Sign in with Google and get started in seconds.
Related Reading
• Elicit AI
• Scholarcy AI
• Scisummary
• AI Research Tools
• Sourcely
• Consensus AI Tool
• Mendeley Alternatives
• Cite This For Me Alternative
• Scholarly Sources Examples
• Academic Sources Examples
• How to Find Scholarly Sources
• List of Scholarly Sources
• Examples of Peer Reviewed Sources
• How to Cite a Book
• How to Cite an Article
• How to Cite
• How to Cite a PDF
• How to Cite Multiple Authors MLA
• How to Cite a Website in Text
• How to Cite a Lecture
• How to Cite ChatGPT
Write more, better, faster.
Your personal AI document assistant